Speed is a fundamental concept in physics and everyday life, playing a crucial role in understanding motion and dynamics. Whether you're in a car, riding a bicycle, or watching a train whiz by, speed helps us quantify how fast an object is moving. It's essential for students, educators, and anyone interested in science to grasp the formula to find speed, as it serves as a building block for more complex topics in physics. This article will explore the various aspects of speed, including its definition, calculation, and real-world applications, making it easier to comprehend and apply.
In the world of physics, speed is defined as the distance traveled by an object per unit of time. It's a scalar quantity, meaning it only has magnitude and no direction. The formula to find speed is simple, yet it unlocks a deeper understanding of motion and kinetics. By exploring the intricacies of speed, we can delve into related concepts such as velocity, acceleration, and time, providing a holistic view of motion. As we journey through this topic, we will cover the practical applications of speed in various fields, from transportation to sports, highlighting its significance in our daily lives.
Understanding the formula to find speed is not only crucial for academic success but also for making informed decisions in real-world scenarios. Whether you're planning a road trip, calculating the best route for a race, or simply trying to improve your personal best in a marathon, knowing how to calculate speed can be invaluable. With the right knowledge, you can enhance your problem-solving skills and gain a better appreciation for the science behind motion. So, let's dive into the fascinating world of speed and discover its many facets and applications.
Read also:Unveiling The Age Of Daniel Radcliffe In Goblet Of Fire A Journey Through Time
Table of Contents
- What is Speed?
- What is the Formula to Find Speed?
- Understanding Speed Units
- How to Calculate Speed?
- Speed vs. Velocity: What's the Difference?
- Practical Applications of Speed
- Speed in Transportation
- Speed in Sports
- The Impact of Speed on Safety
- Technological Advancements and Speed
- Formulas and Equations Related to Speed
- Speed and Acceleration: How Are They Related?
- How Does Speed Differ in Various Media?
- Common Misunderstandings About Speed
- Frequently Asked Questions
- Conclusion
What is Speed?
Speed is a core concept in physics, representing the rate at which an object covers a particular distance. It's a measure of how fast something is moving, irrespective of its direction. As a scalar quantity, speed only considers the magnitude of motion, not its direction. For instance, if a car travels 100 kilometers in two hours, its speed is 50 kilometers per hour (km/h). This straightforward calculation is foundational in understanding more complex physical phenomena.
The significance of speed extends beyond academic exercises, as it plays a vital role in various fields, including engineering, transportation, sports, and even daily activities. Understanding speed allows us to design safer vehicles, optimize travel routes, and improve athletic performance. Additionally, speed is a critical factor in scientific research, enabling the study of celestial bodies, subatomic particles, and everything in between.
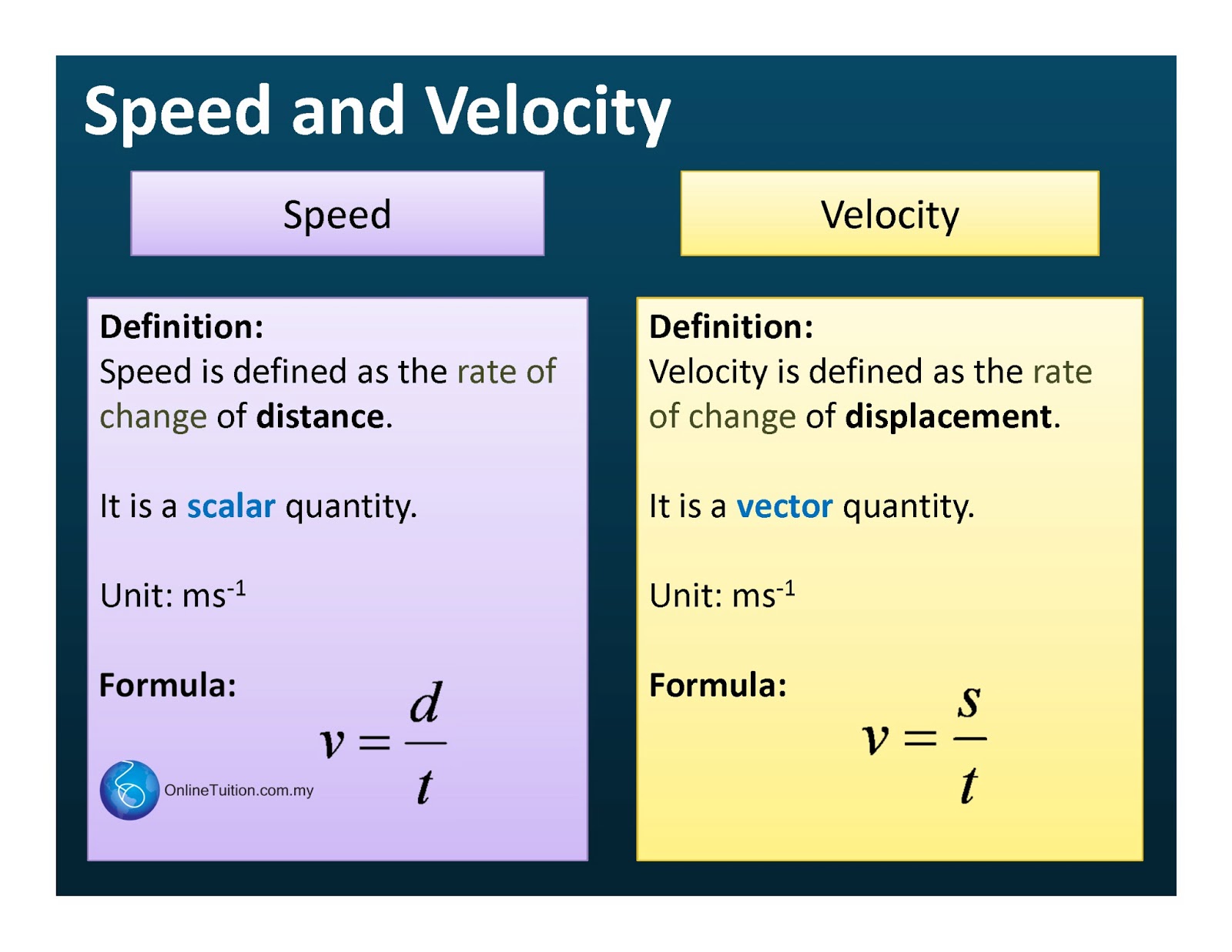
Speed is often confused with velocity, but they differ in a crucial way: velocity is a vector quantity, meaning it has both magnitude and direction. While speed tells us how fast an object is moving, velocity informs us about its speed and the direction of movement. This distinction is fundamental in physics, as it affects how we analyze motion and predict future positions of moving objects.
What is the Formula to Find Speed?
The formula to find speed is a straightforward mathematical equation: Speed = Distance / Time. This formula can be applied to any situation where you need to calculate the speed of an object, provided you know the distance it has traveled and the time it took to do so. This formula is not only simple but also incredibly versatile, forming the basis for more complex equations in physics.
To use the formula to find speed, you'll need two key pieces of information: the distance traveled and the time taken. The distance is typically measured in meters (m) or kilometers (km), while time is measured in seconds (s) or hours (h). By dividing the distance by the time, you can determine the speed of an object in meters per second (m/s) or kilometers per hour (km/h), depending on the units used.
In practical terms, the formula to find speed is invaluable in a wide range of applications. Whether you're measuring the speed of a car on a highway, a runner on a track, or a spacecraft traveling through space, this formula provides a consistent and reliable method for calculating speed. It serves as a foundation for understanding motion and is a critical tool in both academic and professional settings.
Read also:Unveiling The Enigma Of Gary Stewart A Journey Through His Life And Legacy
Understanding Speed Units
Speed is commonly expressed in units that reflect the distance traveled over a specific period of time. The most frequently used units for speed are meters per second (m/s) and kilometers per hour (km/h). Each unit has its own advantages and is suited to different contexts, making it important to understand how they relate to one another.
Meters per second (m/s) is the standard unit of speed in the International System of Units (SI). It's often used in scientific and engineering contexts, where precision and consistency are paramount. This unit provides a clear and concise way to express speed, ensuring that measurements are easily comparable across different studies and experiments.
Kilometers per hour (km/h) is another widely used unit of speed, particularly in everyday situations like driving and cycling. This unit is more intuitive for most people, as it aligns with common experiences and perceptions of speed. For instance, speed limits on roads and highways are typically expressed in kilometers per hour, making it easier for drivers to understand and comply with traffic regulations.
Converting between these units is a straightforward process, requiring a simple multiplication or division. To convert from meters per second to kilometers per hour, multiply the speed by 3.6. Conversely, to convert from kilometers per hour to meters per second, divide the speed by 3.6. This conversion factor stems from the relationship between meters and kilometers, as well as seconds and hours.
How to Calculate Speed?
Calculating speed is a fundamental skill that can be applied in various situations, from academic exercises to real-world scenarios. To calculate speed, you'll need to know two key pieces of information: the distance traveled and the time taken. Once you have these values, you can use the formula to find speed: Speed = Distance / Time.
Let's consider an example to illustrate how to calculate speed. Suppose a cyclist travels a distance of 20 kilometers in 1 hour. To find the speed, divide the distance by the time: 20 km / 1 h = 20 km/h. This calculation tells us that the cyclist's speed is 20 kilometers per hour, providing a clear measure of how fast they are moving.
In some cases, you may need to calculate speed using different units, such as meters per second. To do this, follow the same process but ensure that the distance and time are expressed in meters and seconds, respectively. For instance, if a runner covers 100 meters in 10 seconds, their speed would be 100 m / 10 s = 10 m/s. This calculation reflects the runner's speed in the SI unit of meters per second.
When calculating speed, it's essential to consider any factors that may affect the accuracy of your measurements. Ensure that your distance and time values are precise and accounted for correctly. Additionally, be mindful of any potential sources of error, such as measurement inaccuracies or environmental conditions that could influence the results.
Speed vs. Velocity: What's the Difference?
Speed and velocity are related concepts in physics, but they differ in a fundamental way. Speed is a scalar quantity, meaning it only has magnitude and no direction. It tells us how fast an object is moving, regardless of its direction. In contrast, velocity is a vector quantity, meaning it has both magnitude and direction. Velocity provides information about an object's speed and the direction in which it's moving.
The distinction between speed and velocity is crucial in physics, as it affects how we analyze motion and predict future positions of moving objects. While speed can be calculated using the formula Speed = Distance / Time, velocity requires additional information about the direction of motion. Velocity is often represented with an arrow, indicating both the magnitude and direction of movement.
Understanding the difference between speed and velocity is essential for solving problems in physics, particularly those involving motion. For example, if two cars are traveling at the same speed but in opposite directions, their velocities will differ. This distinction is important when calculating relative motion, determining collision courses, and analyzing the effects of forces on moving objects.
In summary, while speed and velocity are closely related, they serve different purposes in the study of motion. Speed provides a measure of how fast an object is moving, while velocity offers a more comprehensive view of motion by including direction. By understanding these concepts, we can better analyze and predict the behavior of objects in motion.
Practical Applications of Speed
The concept of speed is not only fundamental in physics but also has numerous practical applications in various fields. Understanding speed allows us to design safer vehicles, optimize travel routes, and improve athletic performance. Additionally, speed is a critical factor in scientific research, enabling the study of celestial bodies, subatomic particles, and everything in between.
In transportation, speed plays a vital role in determining travel times, fuel efficiency, and safety. By calculating the speed of vehicles, we can optimize routes, reduce congestion, and enhance the overall efficiency of transportation systems. Speed limits are established to ensure safety on roads and highways, preventing accidents and minimizing the risk of injuries.
In sports, speed is a key performance indicator, influencing the outcomes of races, competitions, and games. Athletes strive to improve their speed to gain a competitive edge, and coaches use speed measurements to assess and enhance performance. Understanding speed allows athletes to set realistic goals, track progress, and develop effective training programs.
Speed is also crucial in scientific research, where it enables the study of phenomena ranging from the motion of planets to the behavior of particles in accelerators. By measuring speed, scientists can gain insights into the underlying principles of motion and develop theories that explain the behavior of matter in the universe.
Speed in Transportation
Speed is a critical factor in the field of transportation, influencing travel times, fuel efficiency, and safety. By calculating the speed of vehicles, we can optimize routes, reduce congestion, and enhance the overall efficiency of transportation systems. Speed limits are established to ensure safety on roads and highways, preventing accidents and minimizing the risk of injuries.
In the automotive industry, speed is a key consideration in the design and manufacturing of vehicles. Engineers work to develop cars, trucks, and buses that can achieve optimal speeds while maintaining safety and fuel efficiency. Advanced technologies, such as cruise control and adaptive speed regulation, help drivers maintain a consistent speed, reducing the risk of accidents and improving fuel economy.
In aviation, speed is a crucial factor in determining flight paths, fuel consumption, and travel times. Pilots and air traffic controllers use speed measurements to coordinate takeoffs, landings, and in-flight maneuvers, ensuring the safety and efficiency of air travel. High-speed trains and magnetic levitation systems also rely on precise speed calculations to provide fast and reliable transportation options.
Speed is also important in maritime transportation, where it affects shipping routes, fuel usage, and delivery times. By calculating the speed of ships, maritime professionals can optimize routes, reduce emissions, and ensure timely deliveries. Understanding speed is essential for navigating challenging conditions, such as strong currents and adverse weather, which can impact the performance of vessels.
Speed in Sports
In the world of sports, speed is a key performance indicator, influencing the outcomes of races, competitions, and games. Athletes strive to improve their speed to gain a competitive edge, and coaches use speed measurements to assess and enhance performance. Understanding speed allows athletes to set realistic goals, track progress, and develop effective training programs.
In track and field events, speed is a primary determinant of success. Sprinters rely on their ability to achieve maximum speed over short distances, while distance runners must maintain a consistent pace to achieve their best times. Speed is also crucial in other sports, such as cycling, swimming, and rowing, where athletes work to optimize their speed to achieve victory.
Team sports, such as soccer, basketball, and hockey, also emphasize speed, as players must quickly move across the field or court to outmaneuver opponents. Speed is a critical component of offensive and defensive strategies, allowing players to create scoring opportunities, intercept passes, and prevent opponents from advancing.
Coaches and trainers use speed measurements to evaluate athletes' performance and develop targeted training programs. By analyzing speed data, they can identify areas for improvement, tailor workouts to individual needs, and monitor progress over time. Understanding speed is essential for maximizing athletic potential and achieving success in competitive sports.
The Impact of Speed on Safety
Speed is a critical factor in ensuring safety in various contexts, from transportation to sports. Understanding the impact of speed on safety allows us to develop strategies and technologies that minimize the risk of accidents and injuries. By controlling speed, we can create safer environments for drivers, passengers, athletes, and pedestrians.
In transportation, speed limits are established to ensure safety on roads and highways. These limits are based on factors such as road conditions, traffic density, and visibility, and are designed to minimize the risk of collisions and injuries. Speeding is a leading cause of traffic accidents, and enforcing speed limits is essential for preventing accidents and saving lives.
Advanced technologies, such as speed cameras and radar detectors, help monitor and regulate speed, ensuring compliance with traffic regulations. In-vehicle safety systems, such as adaptive cruise control and automatic emergency braking, also play a crucial role in maintaining safe speeds and preventing accidents.
In sports, understanding the impact of speed on safety allows athletes to train effectively and minimize the risk of injuries. Coaches and trainers emphasize proper technique and conditioning to help athletes manage speed and avoid accidents. Protective equipment, such as helmets and padding, also plays a vital role in ensuring safety during high-speed activities.
Technological Advancements and Speed
Technological advancements have significantly influenced the way we understand and utilize speed in various fields. From transportation to sports, innovations have enabled us to achieve higher speeds, improve safety, and enhance performance. By harnessing technology, we can optimize speed and unlock new possibilities in numerous applications.
In the automotive industry, advancements in engine design, aerodynamics, and materials have enabled vehicles to achieve higher speeds while maintaining safety and fuel efficiency. Technologies such as turbocharging, variable valve timing, and lightweight materials have revolutionized the way cars are designed and manufactured, allowing for faster and more efficient transportation options.
In aviation, technological innovations have enabled the development of supersonic and hypersonic aircraft, capable of traveling at speeds exceeding the speed of sound. These advancements have the potential to revolutionize air travel, reducing flight times and expanding the possibilities for global transportation. Unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs) and drones also rely on advanced technology to achieve precise speed control and perform complex tasks.
In sports, technology has transformed the way athletes train and compete. Wearable devices, such as GPS watches and heart rate monitors, provide real-time speed data, allowing athletes to optimize their training and performance. Advanced materials and equipment, such as carbon fiber bicycles and aerodynamic swimwear, also play a crucial role in enhancing speed and achieving success in competitive sports.
Formulas and Equations Related to Speed
The formula to find speed is just one of many equations related to motion and kinetics. Understanding these formulas allows us to analyze and predict the behavior of moving objects, providing insights into the principles of physics. By mastering these equations, we can solve complex problems and gain a deeper understanding of the world around us.
In addition to the formula for speed (Speed = Distance / Time), other related equations include those for velocity, acceleration, and momentum. Velocity is calculated using the formula Velocity = Displacement / Time, which considers both the magnitude and direction of motion. Acceleration, the rate of change of velocity, is calculated using the formula Acceleration = Change in Velocity / Time.
Momentum, a measure of an object's motion, is calculated using the formula Momentum = Mass × Velocity. This equation is essential for understanding collisions and the transfer of motion between objects. By analyzing momentum, we can predict the outcomes of interactions between moving objects and develop strategies to optimize motion.
These formulas and equations provide a framework for understanding motion and kinetics, enabling us to analyze a wide range of phenomena in physics. By mastering these concepts, we can solve complex problems and gain a deeper appreciation for the principles that govern the behavior of matter and energy.
Speed and Acceleration: How Are They Related?
Speed and acceleration are closely related concepts in physics, both of which describe aspects of motion. While speed measures the rate at which an object covers a particular distance, acceleration measures the rate at which an object's velocity changes over time. Understanding the relationship between these two concepts is essential for analyzing motion and predicting the behavior of moving objects.
Acceleration is a vector quantity, meaning it has both magnitude and direction. It describes how quickly an object's velocity changes, either by increasing or decreasing speed or by changing direction. The formula for calculating acceleration is Acceleration = Change in Velocity / Time, where the change in velocity is the difference between the final and initial velocities.
When an object is accelerating, its speed is either increasing or decreasing. Positive acceleration indicates an increase in speed, while negative acceleration (also known as deceleration) indicates a decrease in speed. By analyzing acceleration, we can gain insights into the forces acting on an object and predict its future motion.
The relationship between speed and acceleration is crucial for understanding motion in various contexts, from transportation to sports. By analyzing these concepts, we can optimize performance, improve safety, and develop strategies for controlling motion.
How Does Speed Differ in Various Media?
The speed of an object can vary depending on the medium through which it is traveling. Different media, such as air, water, and solid surfaces, can affect the speed of an object due to factors such as friction, resistance, and density. Understanding how speed differs in various media is essential for optimizing motion and performance in different contexts.
In air, speed is influenced by factors such as air resistance and drag. These forces act against the motion of an object, slowing it down and affecting its speed. In aviation, understanding the effects of air resistance is crucial for designing efficient aircraft and optimizing flight paths. Similarly, in sports such as cycling and running, athletes must account for air resistance when striving to achieve their best times.
In water, speed is affected by factors such as buoyancy, drag, and water resistance. Swimmers and boats must contend with these forces to achieve optimal speeds. In competitive swimming, understanding the effects of water resistance is essential for developing effective techniques and achieving success in races.
On solid surfaces, speed is influenced by factors such as friction and surface texture. In transportation, understanding the effects of friction is crucial for optimizing vehicle performance and ensuring safety. In sports, athletes must account for surface conditions when striving to achieve their best speeds.
Common Misunderstandings About Speed
Despite its simplicity, the concept of speed is often misunderstood or misinterpreted. Common misunderstandings can lead to errors in calculations and misinterpretations of motion. By addressing these misconceptions, we can develop a clearer understanding of speed and its applications.
One common misunderstanding is the confusion between speed and velocity. While both describe aspects of motion, they differ in a crucial way: speed is a scalar quantity, while velocity is a vector quantity. This distinction is important for accurately analyzing motion and predicting future positions of moving objects.
Another common misunderstanding is the assumption that speed is always constant. In reality, speed can vary due to factors such as acceleration, deceleration, and changes in direction. Understanding the factors that influence speed is essential for accurately analyzing motion and predicting the behavior of moving objects.
Finally, some people mistakenly believe that speed is the only factor influencing motion. In reality, other factors, such as mass, force, and friction, also play a role in determining how objects move. Understanding these factors is crucial for developing a comprehensive understanding of motion and kinetics.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the formula to find speed?
The formula to find speed is Speed = Distance / Time. This formula can be used to calculate the speed of an object by dividing the distance traveled by the time taken.
How do you calculate speed in different units?
To calculate speed in different units, ensure that the distance and time are expressed in the desired units. For example, to calculate speed in meters per second (m/s), use meters for distance and seconds for time. To convert between kilometers per hour (km/h) and meters per second (m/s), use the conversion factor of 3.6.
What is the difference between speed and velocity?
Speed is a scalar quantity that measures how fast an object is moving, while velocity is a vector quantity that includes both magnitude and direction. Velocity provides information about an object's speed and the direction of movement.
How does speed affect safety?
Speed affects safety by influencing the risk of accidents and injuries. Higher speeds increase the likelihood of collisions and the severity of injuries. Speed limits and safety technologies help regulate speed and minimize risks.
What factors influence speed in different media?
Factors such as friction, resistance, and density influence speed in different media. In air, speed is affected by air resistance and drag. In water, buoyancy and water resistance play a role. On solid surfaces, friction and surface texture impact speed.
What are some common misunderstandings about speed?
Common misunderstandings about speed include confusing it with velocity, assuming speed is always constant, and overlooking other factors influencing motion. Addressing these misconceptions is essential for accurately analyzing and understanding motion.
Conclusion
Understanding the formula to find speed is essential for grasping the fundamental principles of motion and kinetics. By mastering this simple yet powerful equation, we can analyze and predict the behavior of moving objects in various contexts, from transportation and sports to scientific research. Speed plays a crucial role in ensuring safety, optimizing performance, and enhancing our understanding of the world around us.
By exploring the intricacies of speed, we gain insights into related concepts such as velocity, acceleration, and time, providing a holistic view of motion. Whether we're calculating the speed of a car, a runner, or a spacecraft, the formula to find speed serves as a reliable tool for quantifying motion and making informed decisions.
As we continue to explore the fascinating world of speed, we unlock new possibilities for innovation, safety, and performance. By understanding and applying the principles of speed, we can navigate the challenges of a rapidly changing world and harness the power of motion to achieve our goals.
Article Recommendations